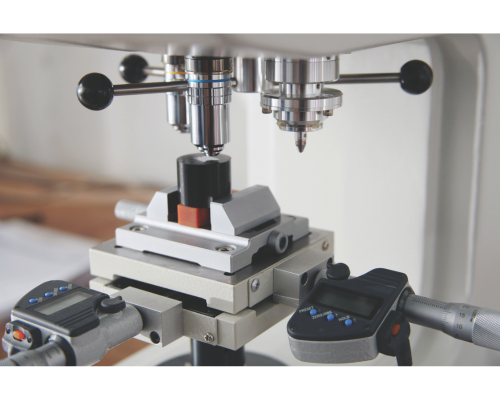

Precision and accuracy have become the two unnegotiable factors in manufacturing today. From aerospace & defence to automotive, medical devices to die & mould industries, the demand for flawless
components has pushed the boundaries of measurement technology. At the forefront of this evolution is 3D metrology, which is redefining how manufacturers inspect, analyse, and ensure the quality of their products with unmatched accuracy and efficiency.
-Kimberley D’Mello
What is 3D Metrology?
3D metrology is the science of measuring objects in three dimensions to capture their precise geometric
data. It verifies components’ dimensions, shape, and surface characteristics using state-of-the-art tools and techniques.
Some 3D Measurement Tools
– Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) measures the geometries of physical objects.
– 3D Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems use advanced imaging techniques to track defects in products.
– Optical Digitizer and Scanner (ODS) uses laser or white light-based scanning technology to capture an object’s geometry by collecting multiple coordinate points, which are then reconstructed into a digital model using specialised software.
– Video Measuring Machine (VMM) is an advanced instrument used for accurate dimensional analysis.
How Does It Work?
The 3D metrology process can be summarised into four key steps:
– Data Collection: In this stage, detailed measurements of a component’s shape, contours, and features are collected.
– Data Processing and Analysis: The collected raw data is then fed into a data processing software to create an accurate 3D model.
– Comparative Analysis: In this stage, the created 3D model is compared with a reference CAD model to check for deviations.
– Visualisation and Reporting: The data acquired from the comparative analysis is then used to generate a comprehensive report summarising the findings.
Industry Applications
3D metrology is essential for industries that demand precision, reliability, and high-performance manufacturing. Some of the key industries that rely on 3D metrology include:
| Industry | Role of 3D Metrology |
| Automotive | Development, production, and testing of automotive components and vehicles, including engines, transmissions, chassis, and body structures. |
| Aerospace | Enabling the precise design, production, and maintenance of aircraft components and systems, including engines, wings, fuselage, and landing gear. |
| Electronics | Inspection and analysis of electronic components and devices, including chips, circuits, circuit boards, and displays. |
| Engineering and Manufacturing | Enabling precise prototyping, tooling, machining, and assembly. It also helps lower costs, boost productivity, and improve the overall quality of both processes and finished products. |
| Healthcare | Manufacturing medical devices, designing orthopedic implants, and patient-specific medical modeling. |
| Plastics | Precisely measure and analyse plastic materials and products, including bottles, containers, and films. It plays a crucial role in determining their properties, characteristics, and overall performance. |
| Tooling | Measure and validate tooling components and equipment, including moulds, dies, fixtures, and gauges. It guarantees accuracy, consistency, and compliance with customer specifications. |
Global Market Overview and Trends
According to a report on the 3D Metrology Market published by the IMARC Group in January 2025:
– The global 3D metrology market is primarily being driven by the increasing focus on improved quality control of manufacturing materials. This factor has led to a rise in investments made in research and development (R&D) activities to introduce 3D metrology technologies for offering enhanced precision during the production process.
– Additionally, the widespread adoption of 3D technology in the automotive and aviation industries to scan and inspect intricate components, digitally recreate parts, and analyse corrosion are further supporting the market growth.
– Other factors, including the employment of cloud computing services, rapid urbanisation, and the
emergence of Industry 4.0, are creating a positive outlook for the market.
The value of global 3D metrology market reached a value of US$11.0 billion in 2024.
Looking forward, the market value is projected to reach USD 21.1 billion by 2033, expanding at a CAGR of 7.5% during 2025-2033.
(Source: 3D Metrology Market Report 2025-2033 by IMARC Group)

Some Emerging Trends and Technologies
– Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): 3D metrology systems are integrated with AI and ML to automate inspection processes. These technologies enhance data analysis by identifying patterns and predicting potential issues, enabling smarter and more efficient measurement processes.
– Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality (AR/VR): When integrated in 3D metrology systems, these technologies can be used to visualise data in an immersive way. They can also enable remote collaboration between engineers and technicians across different locations.
– Cloud Computing: Cloud-based platforms provide secure, centralised access to measurement data from any location, enabling seamless collaboration, data sharing, and remote analysis.
– Industry 4.0: Leveraging advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, and automation, among others, enables real-time data gathering and analysis, supporting predictive maintenance and enhancing the overall production efficiency of 3D metrology systems.
– High-Resolution Scanning Technologies: These technologies are enabling faster and more accurate data
capture. By generating detailed 3D models, they are enhancing the efficiency and precision of analysis and inspection workflows.
– Digital Twin Technology: 3D scanning technology is used to create digital twins. By collecting data points from the surface of a physical object, this technology generates a fully digitised model, or digital twin, in the 3D digital space.
Images used for representation only. Courtesy Envato Elements.
This article was published in TAGMA Times Magazine



COMMENTS